TARS System: Difference between revisions
John Stanton (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
John Stanton (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
* {{IG-TARS Audit}} | * {{IG-TARS Audit}} | ||
* {{GAO-17-152}} | * {{GAO-17-152}} | ||
* {{TARS-PM-2012}} | |||
* [http://www.af.mil/information/factsheets/factsheet.asp?id=3507 USAF Fact Sheet - Tethered Aerostat Radar System 29 Mar 2010] | * [http://www.af.mil/information/factsheets/factsheet.asp?id=3507 USAF Fact Sheet - Tethered Aerostat Radar System 29 Mar 2010] | ||
* [https://www.cbp.gov/sites/default/files/assets/documents/2017-Feb/FS_2017_TARS_FINAL.pdf CBP Fact Sheet - Air and Marine Operations Tethered Aerostat Radar System] | * [https://www.cbp.gov/sites/default/files/assets/documents/2017-Feb/FS_2017_TARS_FINAL.pdf CBP Fact Sheet - Air and Marine Operations Tethered Aerostat Radar System] | ||
Revision as of 09:15, 8 November 2019
|
TARS surveillance data also supports the North American Aerospace Defense Command's (NORAD) air sovereignty mission for the Continental United States (CONUS). The TARS system feeds radar track data for the western sites (TX, NM, AZ) to the Western Air Defense Sector (WADS) at Joint Base Lewis-McChord in Washington State and the radar track data for the eastern and Carribean sites (FL, BH, PR} to the Eastern Air Defense Sector (EADS) in Rome, New York.  HistoryThe TARS program began as three different Aerostat systems one run by the U.S. Air Force, one by the U.S. Customs Service and one by the U.S. Coast Guard. In 1992 Congress mandated a single system to be managed by the U.S. Air Force that would provide radar data to each of the stakeholders. Since none of the systems had gone through the formal acquisition process, support was almost nonexistent and the systems began to fail. At one point five of the eight sites had been down for 28 months. Dissatisfied workers and contractors complained to the DoD IG and an audit was conducted that surfaced the major issues and a management system was put in place. By 2000 a standard system had been defined, contracted for and installations were beginning. The standard system included two different sized balloons, one 275K balloon and the rest as 420K ballons. The radars were standardized to the Lockheed Martin L-88 radar series. The first installation of the standardized system was at the Deming NM site in 2000. 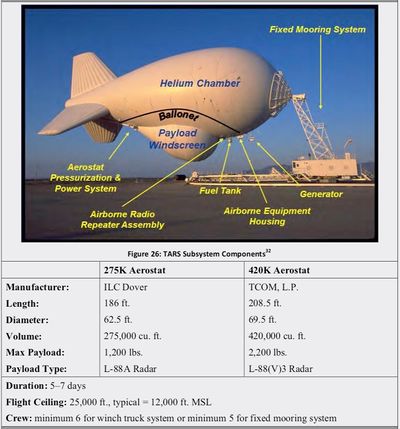 
See Also:
Sources:
Links: |