Fort Welles: Difference between revisions
Bill Thayer (talk | contribs) |
Bill Thayer (talk | contribs) link to account of the battle of Port Royal |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
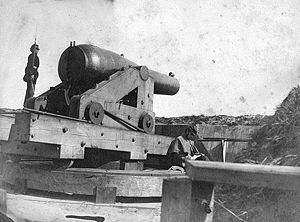
Initially built in 1861 as [[Fort Walker (2)]], a Confederate earthworks fortification, with 16 guns, on the strategic entrance to Port Royal Sound in South Carolina. Fort Walker and [[Fort Beauregard (3)]] on the other side of the entrance to the sound were attacked and overwhelmed by a large Union fleet of fifty ships in November 1861. Fort Walker was subdued by heavy bombardment from the fleet followed by the landing of 13,000 Union troops who surrounded and laid siege to the fort. Union forces occupied the fort for the remainder of the war and significantly expanded it into an system of earthworks almost two miles long. | Initially built in 1861 as [[Fort Walker (2)]], a Confederate earthworks fortification, with 16 guns, on the strategic entrance to Port Royal Sound in South Carolina. Fort Walker and [[Fort Beauregard (3)]] on the other side of the entrance to the sound were attacked and overwhelmed by a large Union fleet of fifty ships in November 1861. Fort Walker was subdued by heavy bombardment from the fleet followed by the landing of 13,000 Union troops who surrounded and laid siege to the fort. Union forces occupied the fort for the remainder of the war and significantly expanded it into an system of earthworks almost two miles long. | ||
=== Further reading === | |||
*[http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Gazetteer/Places/America/United_States/Navy/_Texts/MERTRS/2*.html#go_for_Port_Royal Merrill, James M., ''The Rebel Shore'', pp31 ff.] | |||
{{Clr}} | {{Clr}} | ||
Revision as of 14:03, 1 January 2018
|
Fort Welles (1861-1865, 1897-1902) - A U.S. Civil War Coastal Fort first established as Fort Walker (2) in 1861 by Confederate forces on Hilton Head, Beaufort County, South Carolina. Renamed by Union forces as Fort Welles in G.O. 29, Headquarters, Expeditionary Corps, Hilton Head, South Carolina, 15 Nov 1861. Named after then U.S. Secretary of the Navy, Gideon Welles. Abandoned in 1865.
U.S. Civil War (1861-1865)Part of the Harbor Defense of Port Royal Sound. 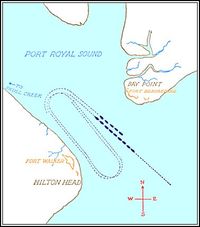 Initially built in 1861 as Fort Walker (2), a Confederate earthworks fortification, with 16 guns, on the strategic entrance to Port Royal Sound in South Carolina. Fort Walker and Fort Beauregard (3) on the other side of the entrance to the sound were attacked and overwhelmed by a large Union fleet of fifty ships in November 1861. Fort Walker was subdued by heavy bombardment from the fleet followed by the landing of 13,000 Union troops who surrounded and laid siege to the fort. Union forces occupied the fort for the remainder of the war and significantly expanded it into an system of earthworks almost two miles long. Further reading
Endicott Period (1890-1910)In 1897 Congress appropriated monies for the purchase of additional experimental compressed air Dynamite guns for emplacement at four coastal fortifications. Hilton Head was chosen to have a single gun emplaced and a concrete battery was built near the location of old Fort Welles. Battery Dynamite (2) was tested and inspected during 1901-1902 but was deactivated and scrapped when the experimental program was discontinued. Current StatusPart of Hilton Head, Beaufort County, South Carolina.
Sources:
Visited: No
| ||||||