Fort Miles: Difference between revisions
John Stanton (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
John Stanton (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SocialNetworks}} | {{SocialNetworks}} | ||
'''{{PAGENAME}}''' (1940-1948) Originally established in 1940 as the [[Cape Henlopen MR|Cape Henlopen Military Reservation(MR)]] and built out as a Coastal Defense Fort. Named for Lt. Gen. [[Nelson Appleton Miles]] on 3 Jun 1941. Coastal Batteries declared surplus 5 May 1948. | '''{{PAGENAME}}''' (1940-1948) Originally established in 1940 as the [[Cape Henlopen MR|Cape Henlopen Military Reservation(MR)]] and built out as a Coastal Defense Fort during [[World War II]]. Named for Lt. Gen. [[Nelson Appleton Miles]] on 3 Jun 1941. Coastal Batteries declared surplus 5 May 1948. | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
{{Clr}} | {{Clr}} | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
{{Clr}} | {{Clr}} | ||
==[[World War II]]== | ==[[World War II]]== | ||
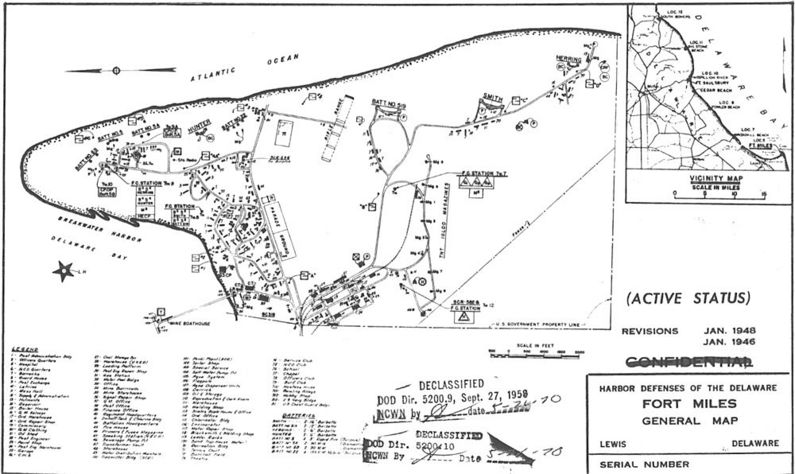
Fort Miles was originally planned to have two 16" gun batteries, [[Batttery 118]] and [[Battery 119]]. Battery 119 was canceled and replaced in 1942 by [[Battery 519]] and armed with two 12" guns from [[Battery Haslet]], [[Fort Saulsbury]]. Two standard 200 series batteries were built, [[Battery 221]] and [[Battery 222]], as well as two Anti-Motor Torpedo Boat batteries, [[Battery AMTB 5A]] and [[Battery AMTB 5B]]. The two AMTB batteries replaced an older 3" battery and provided a more reliable, higher rate of fire capability. | |||
Two sets of four emplacements were also built for 8" railway guns. These emplacements were large U shaped sand revetments with railroad tracks built through the rear. The 16" guns and the eight 8" railway guns gave Fort Miles tremendous firepower and made it a very powerful coastal fort. | |||
At peak strength, Fort Miles had over 2200 personnel assigned from many different units. To support these personnel several periods of base construction were required, the first in 1940 and another in 1942. Many temporary barracks and other facilities were constructed during during these periods and some of these remain today. | |||
== Current Status == | == Current Status == | ||
In 1961 part of the reservation became Fort Miles Army Recreation Area. Defense Department transfered 564 acres to the State of Delaware for Cape Henlopen State Park in 1964. By 1996 the State Park had acquired all of the reservation. Some period guns and some mounts are on display. | In 1961 part of the reservation became Fort Miles Army Recreation Area. Defense Department transfered 564 acres to the State of Delaware for Cape Henlopen State Park in 1964. By 1996 the State Park had acquired all of the reservation. Some period guns and some mounts are on display. | ||
Revision as of 14:21, 14 March 2009
Fort Miles (1940-1948) Originally established in 1940 as the Cape Henlopen Military Reservation(MR) and built out as a Coastal Defense Fort during World War II. Named for Lt. Gen. Nelson Appleton Miles on 3 Jun 1941. Coastal Batteries declared surplus 5 May 1948.
Fort Miles History
Part of Harbor Defenses of the Delaware.
| Battery Click on Battery links below |
No. | Caliber | Type Mount | Service Years | Battery Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Battery 118 Battery Smith (3) |
2 | 16" | Casemated Barbette (CBC) | 1941-1942-1943-1948 | $ 1,326,000 | Navy Guns |
| Battery 119 | 2 | 16" | Casemated Barbette (CBC) | Not Built | $ ? | |
| Battery 519 | 2 | 12" | Casemated Barbette (CBC) | 1942-1943-1944-1948 | $ 857,000 | Guns from Battery Haslet, Fort Saulsbury |
| Battery 20 Battery Railway A |
4 | 8" | Railway | 1942-1942-1944-1944 | $ 47,000 | Navy Guns |
| Battery 21 Battery Railway B |
4 | 8" | Railway | 1942-1942-1944-1944 | $ 50,000 | Navy Guns |
| Battery 221 Battery Herring |
2 | 6" | Shielded Barbette (SBC) |
1942-1943-1944-1948 | $ 181,300 | |
| Battery 222 Battery Hunter (1) |
2 | 6" | Shielded Barbette (SBC) |
1942-1943-1943-1947 | $ 150,200 | |
| Battery 22 | 4 | 155mm | Mobile | 1941-1942-1944-1944 | $ 21,480 | |
| Battery AMTB 5A - Fort Miles | 2 2 |
90mm 90mm |
Fixed Pedestal Mobile |
1943-1943-1943-1946 | $ 11,000 | Mostly Buried |
| Battery AMTB 5B - Fort Miles | 2 2 |
90mm 90mm |
Fixed Pedestal Mobile |
1943-1943-1943-1946 | $ 11,000 | 1 Block covered by parking lot |
| Battery 5 | 4 | 3" | Barbette | 1942-1942-1943-1946 | $ 1,400 | |
| Source: CDSG | ||||||
World War II
Fort Miles was originally planned to have two 16" gun batteries, Batttery 118 and Battery 119. Battery 119 was canceled and replaced in 1942 by Battery 519 and armed with two 12" guns from Battery Haslet, Fort Saulsbury. Two standard 200 series batteries were built, Battery 221 and Battery 222, as well as two Anti-Motor Torpedo Boat batteries, Battery AMTB 5A and Battery AMTB 5B. The two AMTB batteries replaced an older 3" battery and provided a more reliable, higher rate of fire capability.
Two sets of four emplacements were also built for 8" railway guns. These emplacements were large U shaped sand revetments with railroad tracks built through the rear. The 16" guns and the eight 8" railway guns gave Fort Miles tremendous firepower and made it a very powerful coastal fort.
At peak strength, Fort Miles had over 2200 personnel assigned from many different units. To support these personnel several periods of base construction were required, the first in 1940 and another in 1942. Many temporary barracks and other facilities were constructed during during these periods and some of these remain today.
Current Status
In 1961 part of the reservation became Fort Miles Army Recreation Area. Defense Department transfered 564 acres to the State of Delaware for Cape Henlopen State Park in 1964. By 1996 the State Park had acquired all of the reservation. Some period guns and some mounts are on display.
|
{"selectable":false,"width":"500"} |
Location: Lewes, Delaware. Maps & Images Lat: 38.7857278 Long: -75.0953561 |
Sources:
- Roberts, Robert B., Encyclopedia of Historic Forts: The Military, Pioneer, and Trading Posts of the United States, Macmillan, New York, 1988, 10th printing, ISBN 0-02-926880-X, page 130-131
- American Forts Network
- North American Forts
Links:
Visited: No
Fort Miles Picture Gallery
|
Click on the picture to see a larger version. Contribute additional pictures - the more the better! |