Red Bluff Air Force Station: Difference between revisions
John Stanton (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
John Stanton (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (47 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{PageHeader}} | {{PageHeader}} | ||
{{SocialNetworks}} | {{SocialNetworks}} | ||
'''{{PAGENAME}}''' (1956-1970) - A [[Cold War]] Air Force Radar Station first established in 1956 near Red Bluff, Tehama County, California. Named Red Bluff Air Force Station after the location. Initially assigned a Permanent ID of SM-157 | '''{{PAGENAME}}''' (1956-1970) - A [[Cold War]] Air Force Radar Station first established in 1956 near Red Bluff, Tehama County, California. Named Red Bluff Air Force Station after the location. Initially assigned a Permanent ID of '''SM-157''' and later a Sage ID of '''Z-157'''. Abandoned by the Air Force in 1970. A portion continues today as [[Red Bluff FAA Radar Site]], FAA ID of '''RBL'''. | ||
{|{{FWpicframe}} | {|{{FWpicframe}} | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
|width="50%"|[[ | |width="50%"|[[File:Red Bluff AFS Ops Bldg.jpg|350px|thumb|left|Former Red Bluff AFS LRR Operations Building.]] | ||
|width="50%"|[[ | |width="50%"|[[File:Red Bluff AFS Rec Hall.jpg|thumb|right|350px|Former Red Bluff AFS Recreation Hall.]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2"|[[ | |colspan="2"|[[File:Red Bluff AFS FAA Radar.jpg|795px|thumb|center|FAA Radar on Former Red Bluff AFS. FPS-6 Tower pads in the foreground.]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
== History == | |||
== History | Established in 1956 and became operational in 1956 as Red Bluff Air Force Station manned by the 859th AC&W Squadron. The station initially had both a Ground-Control Intercept (GCI) and an early warning mission. The early warning mission involved tracking and identifying all aircraft entering their airspace while the GCI mission involved guiding Air Force interceptors to any identified enemy aircraft. Controllers at the station vectored fighter aircraft at the correct course and speed to intercept enemy aircraft using voice commands via ground-to-air radio. | ||
Established in 1956 and became operational in 1956 as Red Bluff Air Force Station manned by the 859th AC&W Squadron. The station initially had both a Ground-Control Intercept (GCI) and early warning | |||
Initial equipment included one [[MPS-8]] | Initial equipment included one [[MPS-8]] height-finder radar and one [[MPS-11]] search radar. | ||
== [[SAGE System]] Transition == | == [[SAGE System]] Transition == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 19: | ||
[[File:Adair AFS Sage Blockhouse - 6.jpg|795px|thumb|center|Former Adair SAGE Direction Center DC-13]] | [[File:Adair AFS Sage Blockhouse - 6.jpg|795px|thumb|center|Former Adair SAGE Direction Center DC-13]] | ||
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" align="center" | {| class="wikitable" width="100%" align="center" | ||
|+ Red Bluff | |+ Red Bluff AFS Direction Centers & Sectors | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Assigned | ! Assigned | ||
! Direction Center | ! Direction Center | ||
! Sector | ! Sector | ||
|- | |||
| 8 Sep 1955 - 1 Mar 1959|| [[Hamilton Manual Direction Center P-48]] || 28th AD | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 1 Mar 1960 - 1 Apr 1966 || [[Adair SAGE Direction Center DC-13]] || Portland ADS | | 1 Mar 1960 - 1 Apr 1966 || [[Adair SAGE Direction Center DC-13]] || Portland ADS | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
| 19 Nov 1969 - 30 Sep 1970 || [[Luke SAGE Direction Center DC-21]] || 26th AD | | 19 Nov 1969 - 30 Sep 1970 || [[Luke SAGE Direction Center DC-21]] || 26th AD | ||
|} | |} | ||
The site began operation as a SAGE site in 1960 initially feeding the [[Adair SAGE Direction Center DC-13]]. The search radar was upgraded to one [[FPS-67]], one [[FPS-6]] height finder and one [[FPS-90 height finder radar. In 1964 Red Bluff became a Joint Use FAA/ADC facility. | The site began operation as a SAGE site in 1960 initially feeding the [[Adair SAGE Direction Center DC-13]]. The search radar was upgraded to one [[FPS-67]], one [[FPS-6]] height-finder, and one [[FPS-90]] height-finder radar. In 1964 Red Bluff became a Joint Use FAA/ADC facility. | ||
== Closure == | == Closure == | ||
Red Bluff AFS and the 859th | The Pentagon announced the closure of Red Bluff AFS and the deactivation of the 859th Radar Squadron on 5 March 1970. The official deactivation date was 30 Sep 1970. A small portion of the site was transferred to the FAA (see below). By the end of 1972, the remainder of the station was transferred to Tehama County, which developed it into Ridgeway County Park. The station's family housing annex was auctioned off to private parties. | ||
== [[Red Bluff FAA Radar Site]] | == [[Red Bluff FAA Radar Site]] == | ||
In 1971, the GATR site and the operations portion of the main station, including the search radar tower and the operations building, were transferred to the FAA | In 1971, the GATR site and the operations portion of the main station, including the search radar tower and the operations building, were transferred to the FAA continued to operate the [[FPS-67|FPS-67B]] search radar as part of the Joint Surveillance System (JSS) into the 1990s. | ||
The | {{FYQ-47Program}} By 1990 the site was equipped with an [[FPS-67|FPS-67B]] search radar and a [[CD-2|CD-2A]] Common Digitizer. The Red Bluff CD-2A was scheduled to receive an upgrade kit to implement three-level weather data processing in June 1992. | ||
{{ModeSSite|Site=Red Bluff|Seq=114|Date=28 Feb 1995}} | |||
==CARSR Radar == | |||
{{CARSRProgram|Site=Red Bluff}} At the time of the CARSR changeout, the legacy radar in place was still the [[FPS-67|FPS-67B]] and the CARSR conversion included a 1561 Antenna. The secondary radar for the site is the [[Mode S]] Beacon set. | |||
{{DecodeARTCCID|FAAID=ZOA}} | |||
== Gap Fillers == | == Gap Fillers == | ||
Red Bluff AFS was responsible for the maintenance of three remote unattended gap filler radar sites. {{GapFillerCommon}} The Red Bluff AFS gap filler radars were located at Janesville, Whitmore and | Red Bluff AFS was responsible for the maintenance of three remote unattended gap-filler radar sites. {{GapFillerCommon}} The Red Bluff AFS gap-filler radars were located at Janesville, Whitmore, and Hayfork, all in California | ||
{{RedBluffAFSGFS}} | |||
== Physical Plant == | == Physical Plant == | ||
The physical plant of the site was divided into | [[File:Red Bluff AFS Housing Area.jpg|thumb|left|300px|Former Red Bluff AFS Housing Area.]] | ||
The physical plant of the site was divided into the main site, a cantonment area, a housing area, and a radio site. The main site housed the operations buildings, the radar towers, and the backup generators. The Cantonment area housed the enlisted barracks, the bachelor officer's quarters, the orderly room, the dining hall, the motor pool, and other support buildings. Apart from the main site was a small 16-unit housing area for married personnel and the Air Force leased an additional 20 homes in Red Bluff. | |||
Recreational facilities included a small swimming pool, a baseball diamond, an NCO club, and a recreation hall/gym. | |||
{{Clr}} | |||
[[File:Red Bluff AFS GATR Site.jpg|300px|thumb|left|Former Red Bluff AFS GATR Site.]] | |||
A separate radio site housed the radio equipment for directing aircraft intercepts. {{GATRSite|AFS=Red Bluff}} | A separate radio site housed the radio equipment for directing aircraft intercepts. {{GATRSite|AFS=Red Bluff}} | ||
{{Clr}} | {{Clr}} | ||
---- | |||
{| width="800px" | {| width="800px" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| valign="top" width=" | | valign="top" width="60%" | | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ Red Bluff AFS Major Equipment List | |+ Red Bluff AFS Major Equipment List | ||
| Line 66: | Line 77: | ||
!Data Systems | !Data Systems | ||
!Radio | !Radio | ||
!IFF/SIF/Beacon | |||
|- | |- | ||
| valign="top" | | | valign="top" | | ||
* [[MPS- | * [[MPS-11]] | ||
* [[FPS-20]] | * [[FPS-20]] | ||
* [[FPS-67]] | * [[FPS-18]] GF | ||
* [[FPS-67|FPS-67B]] FAA | |||
* [[CARSR]] FAA | |||
| valign="top" | | | valign="top" | | ||
* [[MPS-8]] | |||
* [[FPS-6]] | * [[FPS-6]] | ||
* [[FPS-6|FPS-6A]] | * [[FPS-6|FPS-6A]] | ||
* [[FPS-90]] | * [[FPS-90]] | ||
| valign="top" | | | valign="top" | | ||
* [[FST-1]] GF | |||
* [[FST-2|FST-2/A/B]] | * [[FST-2|FST-2/A/B]] | ||
* [[FYQ-47]] FAA | |||
* [[CD-2|CD-2A]] FAA | |||
| valign="top"| | | valign="top"| | ||
* [[GKA-5]] | * [[GKA-5]] | ||
| valign="top"| | |||
* [[Mode S]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
| valign="top" width=" | | valign="top" width="40%" | | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ Unit Designations | |+ Unit Designations | ||
| Line 95: | Line 114: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
* 8 Sep 1955 - Activated at Hamilton AFB, CA, assigned to 28th AD. | * 8 Sep 1955 - Activated at Hamilton AFB, CA, assigned to 28th AD. ([[Hamilton Manual Direction Center P-48]]) | ||
* Spring 1956 - Moved to Red Bluff AFS, CA. | * Spring 1956 - Moved to Red Bluff AFS, CA. | ||
* 1 Mar 1959 - Transferred to 25th AD. | * 1 Mar 1959 - Transferred to 25th AD. ([[McChord Manual Direction Center P-4]]) | ||
* 1 Mar 1960 - Transferred to Portland ADS. (Adair) | * 1 Mar 1960 - Transferred to Portland ADS. ([[Adair SAGE Direction Center DC-13]]) | ||
* 15 Jul 1960 - Redesignated from AC&W Sq to 859th Radar Sq (SAGE). | * 15 Jul 1960 - Redesignated from AC&W Sq to 859th Radar Sq (SAGE). | ||
* 1 Apr 1966 - Transferred to 26th AD. (Adair) | * 1 Apr 1966 - Transferred to 26th AD. ([[Adair SAGE Direction Center DC-13]]) | ||
* 15 Sep 1969 - Reassigned to 27th AD. (Luke) | * 15 Sep 1969 - Reassigned to 27th AD. ([[Luke SAGE Direction Center DC-21]]) | ||
* 19 Nov 1969 - Reassigned to 26th AD. (Luke) | * 19 Nov 1969 - Reassigned to 26th AD. ([[Luke SAGE Direction Center DC-21]]) | ||
* 30 Sep 1970 - Inactivated. | * 30 Sep 1970 - Inactivated. | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{RedBluffAFSCmdrs}} | |||
== Current Status == | == Current Status == | ||
Abandoned in | [[File:Ridgway Park Sign.jpg|thumb|left|300px|Ridgway Park Sign.]] | ||
Abandoned as an Air Force Station. The old cantonment area is now Ridgeway park and the operations area is an FAA Radar Site. The housing area is in private hands and is a part of a larger housing complex. The GATR radio site is intact but repurposed. | |||
The metal cantonment area buildings (Butler-type buildings) were largely sold off and removed when the site transitioned to the FAA. The foundations remain for the most part. The old-style barracks buildings were totally removed with no remains. The firehouse and the recreation building remain in use. | |||
{{Clr}} | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Red Bluff AFS Fire Sta.jpg|Former Red Bluff AFS Fire House. | |||
File:Red Bluff AFS Gate House Pad.jpg|Gate House Foundation. | |||
File:Red Bluff AFS Auto Shop.jpg|Auto Shop Foundation. | |||
File:Red Bluff AFS Pwr Bldg.jpg|Power Building Foundation. | |||
File:Red Bluff AFS Dining Hall Fnd.jpg|Dining Hall Foundation. | |||
File:Red Bluff AFS Radio Site.jpg|Radio Site/Commissary. | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[File:Red Bluff AFS Composite Plan.png|thumb|center|800px|Red Bluff Air Force Station Composite Plan.]] | |||
{{Clr}} | |||
{{RedBluffAFSStructures}} | |||
---- | ---- | ||
{| | {| | ||
| | | | ||
<googlemap version="0.9" lat="40.14611" lon="-122.30444" zoom="16" width="500" scale="yes" overview="yes" controls="large" icons="http://www.fortwiki.com/mapicons/icon{label}.png"> | <googlemap version="0.9" lat="40.14611" lon="-122.30444" zoom="16" width="-500" height="-500" scale="yes" overview="yes" controls="large" icons="http://www.fortwiki.com/mapicons/icon{label}.png"> | ||
( | (H) 40.16633, -122.2581, Housing Area | ||
( | (G) 40.14443, -122.29037, GATR Site | ||
(C) 40.14642, -122.30616, Cantonment Area | |||
(O) 40.14636, -122.30452, Operations Area | |||
</googlemap> | </googlemap> | ||
|valign="top"| | |valign="top"| | ||
'''Location:''' Red Bluff in Tehama County, California. | '''Location:''' Near Red Bluff in Tehama County, California. Zoom out to see the housing area and the GATR site map points. | ||
{{Mapit-US-cityscale|40.14611|-122.30444}} | {{Mapit-US-cityscale|40.14611|-122.30444}} | ||
| Line 132: | Line 166: | ||
* [[Permanent System Radar Sites]] | * [[Permanent System Radar Sites]] | ||
* [[US Radar Sets]] | * [[US Radar Sets]] | ||
* [[Hamilton Manual Direction Center P-48]] | |||
* [[McChord Manual Direction Center P-4]] | |||
* [[Adair SAGE Direction Center DC-13]] | * [[Adair SAGE Direction Center DC-13]] | ||
* [[Luke SAGE Direction Center DC-21]] | |||
* [[Oakland ARTCC]] | |||
'''Sources:''' | '''Sources:''' | ||
* {{Cornett}}, page 172. <!--ADC Organization--> | * {{Cornett}}, page 172. <!--ADC Organization--> | ||
* {{Winkler}}, page 105. <!--Searching the skies--> | * {{Winkler}}, page 105. <!--Searching the skies--> | ||
{{FAA-CommonSitePrograms}} | |||
* {{GNIS|ID=2086565}} | * {{GNIS|ID=2086565}} | ||
'''Links:''' | '''Links:''' | ||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Red_Bluff_Air_Force_Station Wikipedia - Red Bluff Air Force Station] | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Red_Bluff_Air_Force_Station Wikipedia - Red Bluff Air Force Station] | ||
* [http://www.militarymuseum.org/RedBluffAFS.html California Military Museum - Red Bluff Air Force Station] | * [http://www.militarymuseum.org/RedBluffAFS.html California Military Museum - Red Bluff Air Force Station] | ||
{{Visited| | {{Visited|26 Aug 2017}} | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| Line 153: | Line 191: | ||
[[Category:California Tehama County]] | [[Category:California Tehama County]] | ||
[[Category:{{PAGENAME}}]] | [[Category:{{PAGENAME}}]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:2017 Research Trip]] | ||
[[Category:Starter Page]] | [[Category:Starter Page]] | ||
[[Category:USAF Radar Sites]] | [[Category:USAF Radar Sites]] | ||
[[Category:SAGE Sites]] | |||
[[Category:JSS Sites]] | [[Category:JSS Sites]] | ||
[[Category:MPS-8]] | [[Category:MPS-8]] | ||
[[Category:FPS-20]] | [[Category:FPS-20]] | ||
[[Category:FPS-67]] | [[Category:FPS-67]] | ||
| Line 165: | Line 202: | ||
[[Category:FPS-6]] | [[Category:FPS-6]] | ||
[[Category:FPS-90]] | [[Category:FPS-90]] | ||
[[Category:FPS-18]] | [[Category:FPS-18]] | ||
[[Category:FST-1]] | [[Category:FST-1]] | ||
[[Category:FST-2]] | [[Category:FST-2]] | ||
[[Category:FYQ-47]] | |||
[[Category:GKA-5]] | [[Category:GKA-5]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:46, 13 October 2022
|
Red Bluff Air Force Station (1956-1970) - A Cold War Air Force Radar Station first established in 1956 near Red Bluff, Tehama County, California. Named Red Bluff Air Force Station after the location. Initially assigned a Permanent ID of SM-157 and later a Sage ID of Z-157. Abandoned by the Air Force in 1970. A portion continues today as Red Bluff FAA Radar Site, FAA ID of RBL.
HistoryEstablished in 1956 and became operational in 1956 as Red Bluff Air Force Station manned by the 859th AC&W Squadron. The station initially had both a Ground-Control Intercept (GCI) and an early warning mission. The early warning mission involved tracking and identifying all aircraft entering their airspace while the GCI mission involved guiding Air Force interceptors to any identified enemy aircraft. Controllers at the station vectored fighter aircraft at the correct course and speed to intercept enemy aircraft using voice commands via ground-to-air radio. Initial equipment included one MPS-8 height-finder radar and one MPS-11 search radar. SAGE System TransitionThe transition of the manual GCI system to the automated SAGE system began with the installation of the FST-2 coordinate data transmitter and search radar upgrades. The FST-2 equipment digitized the radar returns and transmitted the digital returns to the SAGE direction center. Under the SAGE System, interceptor aircraft were directed to their targets by the direction center computers and controllers, greatly reducing the need for local controllers and equipment at every radar station. The FST-2 was a very large digital system using vacuum tube technology. Over 6900 vacuum tubes were used in each FST-2 requiring 21 air-conditioned cabinets, 40 tons of air conditioning, 43.5 kva of prime power, and usually a large new addition to the operations building. The FST-2B modification added two more cabinets but with newer solid-state (transistor) technology to process coded responses from aircraft transponders. SAGE System Operation
The site began operation as a SAGE site in 1960 initially feeding the Adair SAGE Direction Center DC-13. The search radar was upgraded to one FPS-67, one FPS-6 height-finder, and one FPS-90 height-finder radar. In 1964 Red Bluff became a Joint Use FAA/ADC facility. ClosureThe Pentagon announced the closure of Red Bluff AFS and the deactivation of the 859th Radar Squadron on 5 March 1970. The official deactivation date was 30 Sep 1970. A small portion of the site was transferred to the FAA (see below). By the end of 1972, the remainder of the station was transferred to Tehama County, which developed it into Ridgeway County Park. The station's family housing annex was auctioned off to private parties. Red Bluff FAA Radar SiteIn 1971, the GATR site and the operations portion of the main station, including the search radar tower and the operations building, were transferred to the FAA continued to operate the FPS-67B search radar as part of the Joint Surveillance System (JSS) into the 1990s. A FYQ-47 Common Digitizer was probably placed in service by February 1973 when the USAF/FAA FST-2 to FYQ-47 replacement program was completed. By 1990 the site was equipped with an FPS-67B search radar and a CD-2A Common Digitizer. The Red Bluff CD-2A was scheduled to receive an upgrade kit to implement three-level weather data processing in June 1992. Mode S Beacon System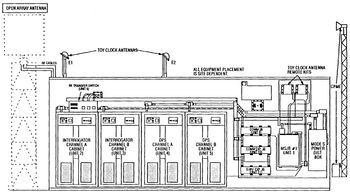 The Red Bluff FAA Radar Site was selected in the 1990s to become one of 21 long-range radar sites to have a Mode S radar beacon system installed. The Mode S system allowed operation in the existing beacon modes but added features to improve beacon operation by allowing aircraft identification with a single interrogation and two-way digital communication between controllers and pilots. Besides the 21 long-range sites, there were other short-range radars to be upgraded for a total of 137 sites on the implementation list. Red Bluff was #114 on the list, scheduled to receive the Mode S equipment on 28 Feb 1995. Installation required interfacing with the radar system, addition of a beacon antenna on top of the search radar antenna, a new larger radome, interfacing with the Common Digitizer (CD-2) if installed, additional communication lines and equipment. CARSR RadarThe nationwide replacement program converting FAA legacy radar systems to the CARSR radar configuration was completed by 17 Aug 2015 and Red Bluff FAA Radar Site was a part of that program. Legacy FAA radars underwent a Service Life Extension Program (SLEP) that replaced key components in the vintage ARSR-1, ARSR-2, FPS-20, FPS-66 and FPS-67 radars. The CARSR program replaced legacy klystron radar transmitters with a solid-state transmitter as well as renovating the radar receiver and signal processor. The CARSR modification also included common digitizer functionality making a separate common digitizer unnecessary. The Red Bluff FAA Radar Site is now operating with the CARSR radar. At the time of the CARSR changeout, the legacy radar in place was still the FPS-67B and the CARSR conversion included a 1561 Antenna. The secondary radar for the site is the Mode S Beacon set. The radar site data is now available to the USAF/NORAD Battle Control System-Fixed (BCS-F) operations centers (EADS & WADS) as well as the FAA Oakland ARTCC (ZOA) and adjacent ARTCCs. Other federal agencies have access to the data under the Homeland Security umbrella. Gap FillersRed Bluff AFS was responsible for the maintenance of three remote unattended gap-filler radar sites. The unattended gap filler sites were placed in locations where the main search radar lacked coverage. These sites were equipped with short range FPS-14 or FPS-18 search radars and FST-1 Coordinate Data transmitters that sent digitized radar target data to a SAGE direction center and to the main radar site. Both the radar set and the FST-1 were dual channel to increase site up time. Maintenance teams were dispatched for regularly scheduled maintenance or when fault indicators on the FSW-1 remote monitoring equipment suggested the site had problems. The FSW-1 also allowed remote operation of specific functions such as channel changes for the radar and for the FST-1, it also allowed remote operation of the diesel generators at the gap filler site. The Red Bluff AFS gap-filler radars were located at Janesville, Whitmore, and Hayfork, all in California
Physical Plant The physical plant of the site was divided into the main site, a cantonment area, a housing area, and a radio site. The main site housed the operations buildings, the radar towers, and the backup generators. The Cantonment area housed the enlisted barracks, the bachelor officer's quarters, the orderly room, the dining hall, the motor pool, and other support buildings. Apart from the main site was a small 16-unit housing area for married personnel and the Air Force leased an additional 20 homes in Red Bluff. Recreational facilities included a small swimming pool, a baseball diamond, an NCO club, and a recreation hall/gym.
 A separate radio site housed the radio equipment for directing aircraft intercepts. Like most early radar stations, Red Bluff originally had a radio transmitter site and a separate radio receiver site used by local controllers for voice direction of fighter interceptors to their targets. With the SAGE System, the SAGE Direction centers had the primary task of directing intercepts and the local radio sites were reconfigured, usually into a single site that was known as the Ground to Air Transmitter Receiver (GATR) site. The GATR site communicated with the interceptors from either the local site or the SAGE direction center via voice commands and/or a digital data link.
Current Status Abandoned as an Air Force Station. The old cantonment area is now Ridgeway park and the operations area is an FAA Radar Site. The housing area is in private hands and is a part of a larger housing complex. The GATR radio site is intact but repurposed. The metal cantonment area buildings (Butler-type buildings) were largely sold off and removed when the site transitioned to the FAA. The foundations remain for the most part. The old-style barracks buildings were totally removed with no remains. The firehouse and the recreation building remain in use.

See Also:
Sources:
Visited: 26 Aug 2017
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||








